Xenophidiidae
| Xenophidiidae[1] | |||
| Wallach & Günther, 1998[2] | |||
| Systematyka | |||
| Domena | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Królestwo | |||
| Typ | |||
| Podtyp | |||
| Gromada | |||
| Podgromada | |||
| Rząd | |||
| Podrząd | |||
| Infrarząd | |||
| Rodzina |
Xenophidiidae | ||
| Typ nomenklatoryczny | |||
|
Xenophidion acanthognathus Günther & Manthey, 1995 | |||
| rodzaje | |||
| |||
| Zasięg występowania | |||
 | |||
Xenophidiidae – monotypowa rodzina węża z infrarzędu Alethinophidia w rzędzie łuskonośnych (Squamata).
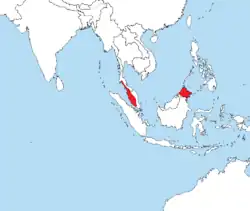
Zasięg występowania
Rodzina obejmuje gatunki występujące w Malezji (Sabah, Sarawak i Malezja Zachodnia) i Indonezji (Sumatra)[4][5].
Systematyka
Etymologia
Xenophidion: gr. ξενος xenos „obcy, dziwny”; οφιδιον ophidion „wężyk, mały wąż”, zdrobnienie od οφις ophis, οφεως opheōs „wąż”[3].
Podział systematyczny
Do rodziny należy jeden rodzaj z następującymi gatunkami[4]:
- Xenophidion acanthognathus
- Xenophidion schaeferi
Przypisy
- ↑ Xenophidiidae, [w:] Integrated Taxonomic Information System (ang.).
- ↑ V.S.B. Wallach & R. Günther. Visceral anatomy of the Malaysian snake genus Xenophidion, including a cladistic analysis and allocation to a new family (Serpentes: Xenophidiidae). „Amphibia-Reptilia”. 19 (4), s. 385–405, 1998. DOI: 10.1163/156853898X00052. (ang.).
- 1 2 R. Günther & U. Manthey. Xenophidion, a new genus with two new species of snakes from Malaysia (Serpentes, Colubridae). „Amphibia-Reptilia”. 16 (3), s. 230, 1995. DOI: 10.1163/156853895X00028. (ang.).
- 1 2 P. Uetz & J. Hallermann: Higher taxa: Xenophidiidae. The Reptile Database. [dostęp 2019-11-29]. (ang.).
- ↑ R. Midtgaard: Xenophidiidae. RepFocus. [dostęp 2019-11-29]. (ang.).