Zootrophion
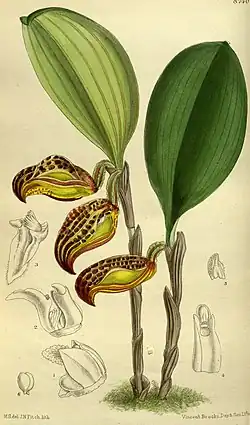 Zootrophion dayanum | |||
| Systematyka[1][2] | |||
| Domena | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Królestwo | |||
| Podkrólestwo | |||
| Nadgromada | |||
| Gromada | |||
| Podgromada | |||
| Nadklasa | |||
| Klasa | |||
| Nadrząd | |||
| Rząd | |||
| Rodzina | |||
| Podrodzina | |||
| Rodzaj |
Zootrophion | ||
| Nazwa systematyczna | |||
| Zootrophion Luer Selbyana 7: 80. 31 Aug 1982.[3] | |||
| Typ nomenklatoryczny | |||
| Synonimy | |||
|
| |||
Zootrophion – rodzaj roślin z rodziny storczykowatych (Orchidaceae). Obejmuje 32 gatunki. Są to epifity o twardych liściach, owalno-jajowatych, do okrągłych i ostro zakończonych. Kwiaty pojedyncze. Rośliny z tego rodzaju występują w mglistych lasach tropikalnych w górach na wysokościach do 2100 m. Rosną we wschodniej i południowo-wschodniej Brazylii, na Kubie, Dominikanie, Haiti, Jamajce, w Kostaryce, Panamie, Boliwii, Kolumbii, Ekwadorze oraz Peru[8].
Systematyka
Rodzaj sklasyfikowany do podplemienia Pleurothallidinae w plemieniu Epidendreae, podrodzina epidendronowe (Epidendroideae), rodzina storczykowate (Orchidaceae), rząd szparagowce (Asparagales) w obrębie roślin jednoliściennych[9][6][10].
- Zootrophion aguirrei P.Ortiz
- Zootrophion alvaroi (Garay) Luer
- Zootrophion antioquianum Uribe Vélez & Sauleda
- Zootrophion argus (Kraenzl.) Luer
- Zootrophion atropurpureum (Lindl.) Luer
- Zootrophion beloglottis (Schltr.) Luer
- Zootrophion dayanum (Rchb.f.) Luer
- Zootrophion disciformis Vierling
- Zootrophion dodsonii (Luer) Luer
- Zootrophion eburneum Rysy
- Zootrophion endresianum (Kraenzl.) Luer
- Zootrophion erlangense Roeth & Rysy
- Zootrophion fenestratum (Lindl. ex Hook.) Rysy
- Zootrophion fritzwalteri Vierling
- Zootrophion gracilentum (Rchb.f.) Luer
- Zootrophion griffin Luer
- Zootrophion hirtzii Luer
- Zootrophion hypodiscus (Rchb.f.) Luer
- Zootrophion ildephonsi P.Ortiz
- Zootrophion lappaceum Luer & R.Escobar
- Zootrophion leonii D.E.Benn. & Christenson
- Zootrophion machaqway A.Doucette & J.Portilla
- Zootrophion muliebre Vierling
- Zootrophion niveum Luer & Hirtz
- Zootrophion oblongifolium (Rolfe) Luer
- Zootrophion serpentinum Luer
- Zootrophion trivalve (Luer & R.Escobar) Luer
- Zootrophion vasquezii Luer
- Zootrophion virginalis Vierling
- Zootrophion vulturiceps (Luer) Luer
- Zootrophion williamsii Luer
- Zootrophion ximenae (Luer & Hirtz) Pfahl
Przypisy
- ↑ Michael A. Ruggiero i inni, A Higher Level Classification of All Living Organisms, „PLOS One”, 10 (4), 2015, art. nr e0119248, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119248, PMID: 25923521, PMCID: PMC4418965 [dostęp 2022-11-16] (ang.).
- ↑ Peter F. Stevens, Angiosperm Phylogeny Website, Missouri Botanical Garden, 2001– [dostęp 2022-11-16] (ang.).
- ↑ Index Nominum Genericorum (ING). Smithsonian Institution. [dostęp 2015-12-14].
- ↑ Zootrophion. Tropicos.org. [dostęp 2015-12-14].
- ↑ Zootrophion. Tropicos.org. [dostęp 2015-12-14].
- 1 2 3 Zootrophion. Kew Royal Botanic Gardens. [dostęp 2015-12-14].
- 1 2 Zootrophion. [w:] The World Checklist of Vascular Plants [on-line]. Catalogue of Life Checklist. [dostęp 2023-06-07].
- ↑ Zootrophion. e-Monocot.org. [dostęp 2015-12-14]. [zarchiwizowane z tego adresu].
- ↑ Zootrophion. Tropicos.org. [dostęp 2015-12-14].
- ↑ Zootrophion. National Center for Biotechnology Information. [dostęp 2023-06-07].
Identyfikatory zewnętrzne (takson):