Diurideae
 | |
| Systematyka[1][2] | |
| Domena | |
|---|---|
| Królestwo | |
| Podkrólestwo | |
| Nadgromada | |
| Gromada | |
| Podgromada | |
| Nadklasa | |
| Klasa | |
| Nadrząd | |
| Rząd | |
| Rodzina | |
| Podrodzina | |
| Plemię |
Diurideae |
| Nazwa systematyczna | |
| Diurideae (Endl.) Lindl. ex Meisn. Pl. Vasc. Gen.: Tab. Diagn. 387, Comm. 289. (1842)[3] | |
| Typ nomenklatoryczny | |
|
Diuris Sm.[3] | |
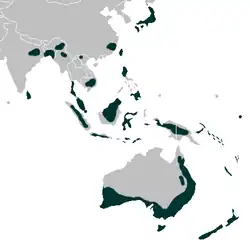
Diurideae – plemię roślin z rodziny storczykowatych (Orchidaceae). Obejmuje 9 podplemion, ponad 30 rodzajów i 1000 gatunków występujących w Azji, Australii i Oceanii[4].
Systematyka
Plemię sklasyfikowane do podrodziny storczykowych (Orchidoideae) w rodzinie storczykowatych (Orchidaceae), rząd szparagowce (Asparagales) w obrębie roślin jednoliściennych[4][5].
- Acianthinae Schltr.
- Caladeniinae Pfitzer
- Cryptostylidinae Schltr.
- Diuridinae Lindl.
- Drakaeinae Schltr.
- Megastylidinae Schltr.
- Prasophyllinae Schltr.
- Rhizanthellinae R.S. Rogers
- Thelymitrinae Lindl.
Przypisy
- ↑ Michael A. Ruggiero i inni, A Higher Level Classification of All Living Organisms, „PLOS One”, 10 (4), 2015, art. nr e0119248, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119248, PMID: 25923521, PMCID: PMC4418965 [dostęp 2022-11-27] (ang.).
- ↑ Peter F. Stevens, Angiosperm Phylogeny Website, Missouri Botanical Garden, 2001– [dostęp 2022-11-27] (ang.).
- 1 2 Index Nominum Genericorum (ING). Smithsonian Institution. [dostęp 2022-11-27].
- 1 2 Diurideae. Tropicos.org. [dostęp 2022-11-27].
- 1 2 Diurideae. NCBI. [dostęp 2022-11-27].
- ↑ Diurideae. NCBI. [dostęp 2022-11-27].
Identyfikatory zewnętrzne (takson):